Areas with heavy reliance on groundwater were identified and designated as Active Management Areas (AMAs). The AMAs were established to provide long-term management and conservation of their limited groundwater supplies. Within AMAs, the Arizona Department of Water Resources administers state laws, develops and implements groundwater management plans, explores ways of augmenting water supplies to meet future needs, and works to develop public policy in order to promote efficient use and an equitable allocation of available water supplies. Statutory management goals for each AMA guide the policies for managing water in these areas. Outside of AMAs, groundwater rights in Arizona are generally tied to ownership of the overlying surface land, meaning they cannot be bought or sold separately from the land. Learn more.
The 1980 Groundwater Management Act includes provisions to help prevent this scenario. Under the Act, there are two kinds of areas in which groundwater is regulated:
1. Irrigation Non-Expansion Areas (INAs) – wells larger than small residential wells are metered, and their groundwater use is reported annually. In addition, there is a prohibition on new irrigated agriculture (defined as two or more acres).
2. Active Management Areas (AMAs) – metering and reporting of groundwater use; prohibition on new irrigated agriculture; developments of six or more homes cannot be platted without proof of a 100-year supply of water that is physically, financially, and legally available. Every ten years, ADWR develops a new management plan for each AMA, with increasingly rigorous conservation and efficiency requirements for all sectors. Agriculture tends to be the biggest water-using sector, and since 1980, new irrigated agriculture has been prohibited within the AMAs and Irrigation Non-Expansion Areas. (No such prohibition is in place outside the AMAs and INAs, which is why some parts of the state have seen an influx of industrial-scale, groundwater-dependent agriculture.) Farms with grandfathered wells are permitted to pump groundwater to irrigate their crops. Energy costs to pump groundwater are a consideration for farmers, particularly as the water table falls and more energy is required to pump it for use. At some point, the energy costs may render some types of irrigated agriculture unprofitable.
Usually, if municipal water is available it is much less expensive and far more reliable than water from an individual private well. Outside AMAs and INAs, there is virtually no regulation on the amount of water a well owner can pump.
Groundwater is water found under the surface of the earth between the pores and fractures of sand, gravel, and rock known as aquifers. We have access to a large groundwater resource and a large aquifer under the Phoenix region, and there are groundwater basins across the state of Arizona. Groundwater needs to be carefully managed because it is largely non-renewable on a human-time scale. Surface water from rivers is renewed by rain and snow, unlike groundwater, which is withdrawn much faster than it is replenished in Arizona. It can take decades, hundreds, or even thousands of years to replenish to the level that we have now. It's important to carefully manage it and look out over 100 years to ensure that groundwater is sustainable over that period. To explore changes in groundwater levels throughout Arizona, use the Arizona Water Blueprint tool created by the Kyl Center for Water Policy, one of the pillars of the Arizona Water Innovation Initiative.
Tools

ASU is innovating agriculture for a more food-secure future
Agriculture is as old as our state — older, in fact — yet today's approaches to our food supply are anything but. From AI drones to supply routes that get produce from farm to table faster, advances in agriculture are…

Groundwater Depletion in the Colorado River Basin
The Colorado River Basin is not just losing surface water. NASA satellites show how the Basin’s groundwater is vanishing, too.

Groundwater Level Changes
An interactive map that shows groundwater level changes across the state's sub-basins for 1-year, 10-year, and 20-year time periods from the Kyl Center for Water Policy.

Rural Groundwater Resilience Toolkit
Providing rural Arizona communities with groundwater resilience guidance, direction, and resources to address local water challenges and strengthen long-term, science-driven solutions. Developed by Impact Water - Arizona…

AMA Data Maps
The Arizona Department of Water Resources Active Management Area (AMA) data maps include the Annual Supply and Demand Dashboard and Agricultural Program water usage.

Private Domestic Well Map
The US Environmental Protection Agency's Private Domestic Well map allows users to search for private domestic wells, utilizing 2020 U.S. estimates
Fact sheets

ASU is innovating agriculture for a more food-secure future
Agriculture is as old as our state — older, in fact — yet today's approaches to our food supply are anything but. From AI drones to supply routes that get produce from farm to table faster, advances in agriculture are…

Annual Water Supply and Demand Estimates
Arizona Department of Water Resources supply and demand assessments of each groundwater basin in the state to improve understanding of the current and future water conditions throughout the state. …

Arizona Water Factsheets
These county-level factsheets from the University of Arizona's Water Resources Research Center are designed to answer common questions about water resources, tailored to every county in Arizona so as to foster…
Research and policy briefs

ASU is innovating agriculture for a more food-secure future
Agriculture is as old as our state — older, in fact — yet today's approaches to our food supply are anything but. From AI drones to supply routes that get produce from farm to table faster, advances in agriculture are…

How Arizona Municipal Water Providers Are Regulating Large-Volume Water Users
Recognizing the need to manage water supplies sustainably and cognizant of public concerns about long-term availability, at least nine large municipal water providers in Arizona have passed ordinances imposing…
Research brief: Declining freshwater availability in the Colorado River Basin threatens sustainability of its critical groundwater supplies
The Colorado River Basin, a crucial water source for several U.S. states and Mexico, is facing a severe and ongoing decrease in freshwater – both surface and groundwater. This decline is mainly due to the changing…

More Elusive Than Ever: Arizona’s Assured Water Supply Protections Under Colorado River Shortages and Groundwater Scarcity
In the state's most urban areas, Arizona's Groundwater Management Act prohibits the sale of subdivision lots that lack a 100-year assured water supply. Allowing groundwater to qualify as an assured supply conflicts with…

Exploratory Scenario Planning for Water Resilient Agriculture
In September 2023, the Babbitt Center, with our partners at the Arizona Water Innovation Initiative at ASU and Lincoln Institute’s Consortium for Scenario Planning, brought together farmers, ranchers, residents,…
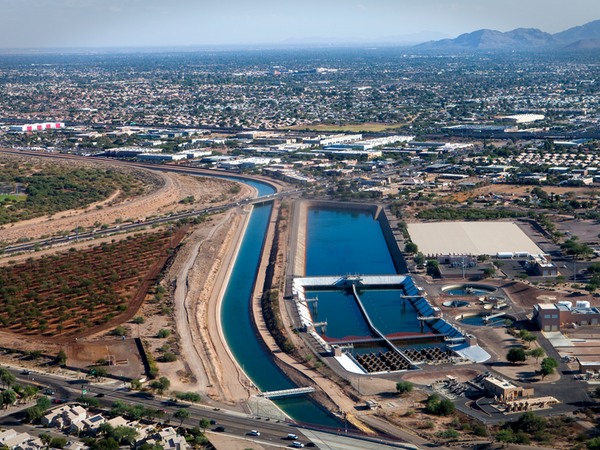

Groundwater Protection in the Valley of the Sun
Sustainable water management is essential in the Valley of the Sun, underpinning public health, economic vitality and quality of life in our desert cities. Underneath the Valley sits an enormous aquifer containing enough…
Newsletters
Interested in keeping up with our events, news, and resources? Sign up for our newsletter today!
Sign up
Videos and webinars

ASU is innovating agriculture for a more food-secure future
Agriculture is as old as our state — older, in fact — yet today's approaches to our food supply are anything but. From AI drones to supply routes that get produce from farm to table faster, advances in agriculture are…

What About Water? podcast
"What About Water? with Jay Famiglietti" connects water science with the stories that bring about solutions, adaptation, and action for the world's water realities. Presented by Arizona State University and the University…

Water Talk podcast
Water Talk brings together communities to explore water issues, including climate change, scarcity, and access. Hosted by Faith Kearns, Mallika Nocco, and Samuel Sandoval.

Agriculture & Water in the West
In September 2023, the Babbitt Center, with our partners at Arizona State University’s Water Innovation Initiative and Lincoln Institute’s Consortium for Scenario Planning, brought together farmers, ranchers, residents,…